Table Of Content

And cysteine is one of just two amino acids that have a high sulfur content (the other being methionine). And perhaps that's partly why the exact mechanism causing hair loss has been a mystery for so long. Below, we’re breaking down the basics of hair anatomy to help you care for your hair from the inside out. Let’s discuss some of the frequently asked questions on microscope hair. If you learn the previous section of the hair perfectly, you may skip this part.
Beyoncé's Hair Colour Includes Expertly Placed Money Pieces — Here's Exactly What Those Are - POPSUGAR United Kingdom
Beyoncé's Hair Colour Includes Expertly Placed Money Pieces — Here's Exactly What Those Are.
Posted: Thu, 06 Jun 2019 07:00:00 GMT [source]
The medulla of a hair under a microscope
In contrast to EDA and EDAR, members of the bone morphogenic protein (BMP) family of secreted signaling molecules seem to be inhibitors of placode formation. The antagonist named Noggin neutralizes BMP activity via regulation of lymphoid enhancer factor 1 (LEF1) expression [4]. Thereafter, the epithelial placode expands and generates the primary hair germ (stage 2). The second signal arises from epithelial placode and constitutes a cluster of adjacent mesenchymal cells which later develops the dermal papilla (DP). The ultimate signal from this primitive dermal papilla to the epithelial placode cells indicates a rapid proliferation and differentiation. This consecutive signaling process finally leads to the production of the mature follicle.
Pearson Correlation Coefficients and Discriminant Validity Download Scientific Diagram - ResearchGate
Pearson Correlation Coefficients and Discriminant Validity Download Scientific Diagram.
Posted: Sat, 11 Jul 2020 02:57:39 GMT [source]
3. Molecular structure
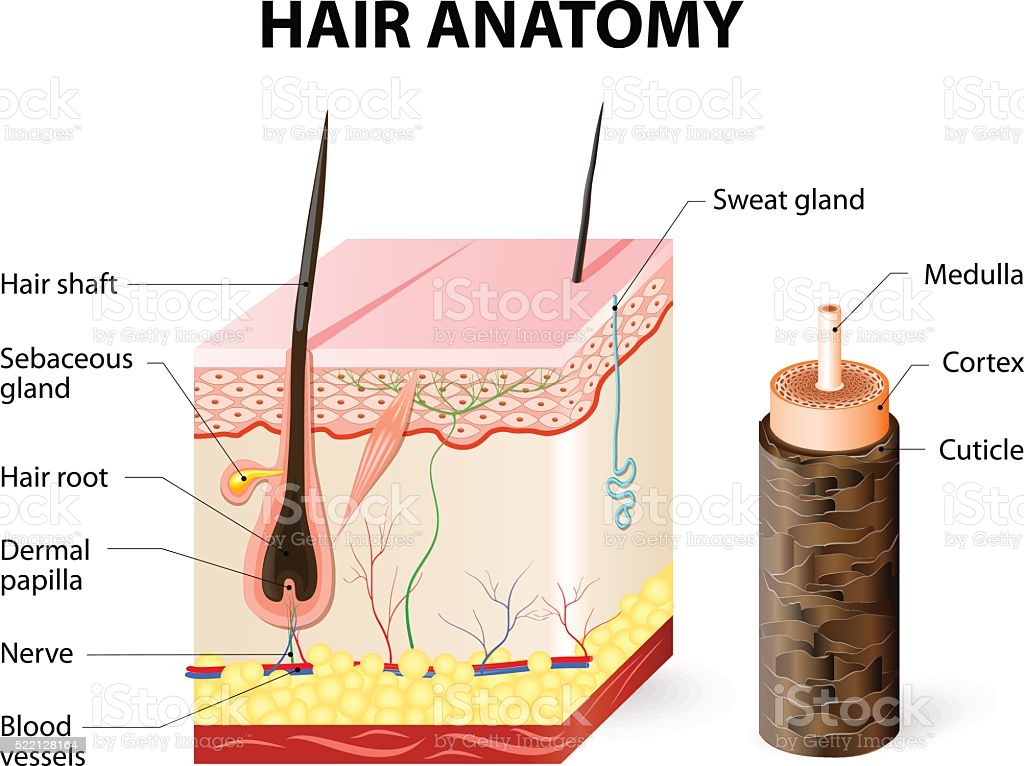
Derived from the epithelial cells of the hair peg, hair matrix cells form the hair shaft and inner root sheath (IRS). During the development of bullous peg (stages 5–8), the hair bulb and the main cell layers of the mature hair follicle are also formed [2–4, 6]. These layers are depicted in a longitudinal cross-section of the hair follicle (Figure 2), although not all hair has a medullary layer.
The Hair Bulb
After producing the new cells, they pass superficially and undergo keratinization. At the lower end of the hair root, these rounded nucleated cells become continuous with the hair bulb. The cells found in the hair bulb also continue with the stratum spinosum of the skin.
You will find numerous ovoid structures with pigment granules in the hair shaft of cattle. These are the long with medium-shaped diameter hair in animals. But, the diameter of this head hair may vary in different animal species. The medulla of the head hair may be absent or continuous and relatively narrow.
During anagen, melanogenesis is activated in the hair bulb and suggests that hair follicle melanocyte autoantigens play a key role as potential immune targets [28, 31]. Until recently, the IP of the hair follicle is considered to be restricted to the matrix region during the anagen phase. However, evidence has accumulated that the IP of the hair follicle extends to the bulge region and is present at this site during the entire hair cycle. Since the bulge represents the hair follicle stem cell niche, sustained IP in this region may be essential for the survival of the follicle.
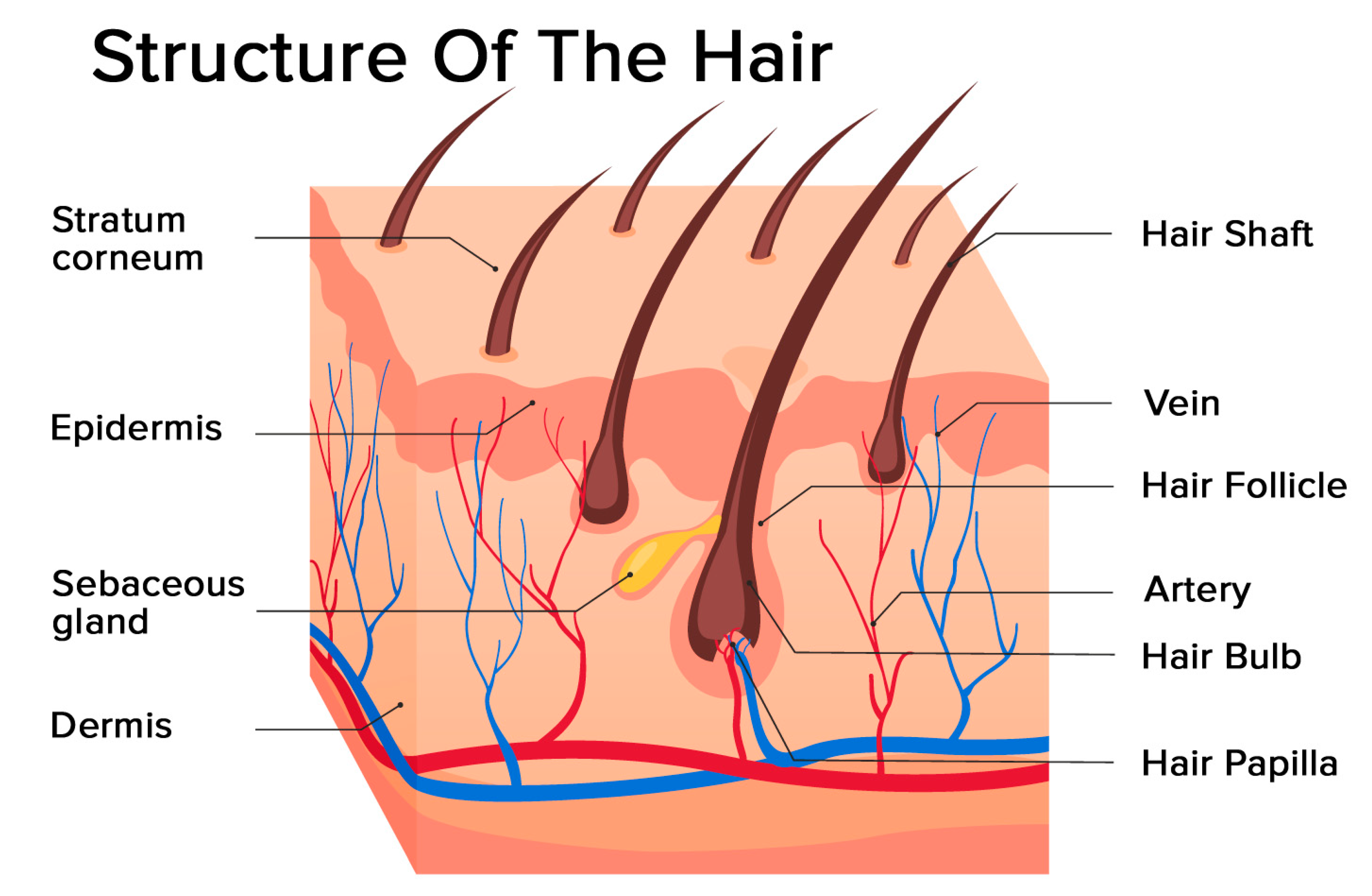
Again, the hair follicle is the epidermis structure that develops as down growth of the epidermis into the dermis and possesses different parts. Hair serves a variety of functions, including protection, sensory input, thermoregulation, and communication. The hair in the nose and ears, and around the eyes (eyelashes) defends the body by trapping and excluding dust particles that may contain allergens and microbes. Hair of the eyebrows prevents sweat and other particles from dripping into and bothering the eyes. Hair also has a sensory function due to sensory innervation by a hair root plexus surrounding the base of each hair follicle.
So, it will be better if you learn these microscopic features with the help of a labeled diagram. At the end of anagen, mitotic activity of the matrix cells is diminished and the follicle enters a highly controlled involutionary phase known as catagen. Catagen lasts approximately 2 weeks in humans, regardless of the site and follicle type [37].
Again, the hair shaft comprises the keratin protein that makes hair both strong and flexible. You will find a similar structural pattern in the keratine protein like all other body proteins. So, there is a chain of amino acids in the helical or spiral arrangement in the keratin protein.
The first sign of catagen is the termination of melanogenesis in the hair bulb. Follicular epithelium, mesenchyme, neuroectodermal cell populations and also perifollicular vascular and neural systems demonstrates cyclic changes in differentiation and apoptosis. However, any apoptosis is occurred in dermal papilla due to the expression of suppressor bcl-2 [11]. The duration of the phases changes based on the location of the hair and also personal nutritional and hormonal status and age [15, 33].
Again, the hair shaft shows three important features – cuticle, cortex, and medulla- that I have already described with the labeled diagrams. The microscopic features of the connective tissue layer of the hair follicle are similar to the normal connective tissue. This connective tissue of the hair follicle is made up of tissue continuous with the dermis of the skin. The outer cell layers also give rise to the inner root layer cells.
The germinatinglayer of the epidermisstarts growing down into the dermis, and forms the outside of each hairfollicle. Biotin (B7) is a water-soluble form of vitamin B that supports hair growth and defends hair from environmental damage. Biotin metabolizes amino acids from foods which helps keratin form in hair and is one of the most popular purported vitamins for hair according to the National Institutes of Health. In fact, as we get older, the number of hair follicles per square inch decreases as our bodies stretch and grow. Because hairs continue to enter the resting phase and then fall out, we are constantly losing hair.
Fine, I will provide some important identifying features of a dog’s hair with its microscopic figure. The diameter of the cat hair is fine, but you may find a little variation in different species of cats. You will find a uniserial ladder continuous medulla in the cat’s hair that occasionally vacuolated. Get more microscope hair-labeled diagrams on social media of anatomy learners. Let’s see the hair shaft; externally, a cuticle covers the hair with a thin membrane. You will easily understand the cuticle layer of hair in the next diagram.
There is an inner root layer that remains inside the outer root layer. This layer contains the softer keratinized cells derived from the cells in the hair matrix. You will also find three layers in the composition of the inner root layer – Huxley’s layer, Henle’s layer, and the outer cuticle layer. The hair follicle is made of multiple layers of cells that form from basal cells in the hair matrix and the hair root. Cells of the hair matrix divide and differentiate to form the layers of the hair.
No comments:
Post a Comment